9.6. Idiom Sorted
sorted(iterable, *, key=None, reverse=False)Sort an iterable and return a new sorted list.
keyspecifies a one-argument ordering function
9.6.1. Sorted
>>> data = [3, 1, 2]
>>>
>>> sorted(data)
[1, 2, 3]
9.6.2. Reverse
>>> data = [3, 1, 2]
>>>
>>> sorted(data, reverse=True)
[3, 2, 1]
9.6.3. Key
>>> USERS = [
... {'firstname': 'Alice', 'lastname': 'Apricot', 'age': 30},
... {'firstname': 'Bob', 'lastname': 'Blackthorn', 'age': 31},
... {'firstname': 'Carol', 'lastname': 'Corn', 'age': 32},
... {'firstname': 'Dave', 'lastname': 'Durian', 'age': 33},
... {'firstname': 'Eve', 'lastname': 'Elderberry', 'age': 34},
... {'firstname': 'Mallory', 'lastname': 'Melon', 'age': 15},
... ]
>>>
>>> def age(user):
... return user['age']
>>>
>>> sorted(USERS, key=age)
[{'firstname': 'Mallory', 'lastname': 'Melon', 'age': 15},
{'firstname': 'Alice', 'lastname': 'Apricot', 'age': 30},
{'firstname': 'Bob', 'lastname': 'Blackthorn', 'age': 31},
{'firstname': 'Carol', 'lastname': 'Corn', 'age': 32},
{'firstname': 'Dave', 'lastname': 'Durian', 'age': 33},
{'firstname': 'Eve', 'lastname': 'Elderberry', 'age': 34}]
9.6.4. Problem
Bubble sort
>>> data = [3, 1, 2]
>>>
>>> def mysorted(data):
... result = data.copy()
... n = len(data)
... for i in range(n):
... for j in range(n-i-1):
... if result[j] > result[j+1]:
... result[j], result[j+1] = result[j+1], result[j]
... return result
>>>
>>> mysorted(data)
[1, 2, 3]
9.6.5. Solution
>>> data = [3, 1, 2]
>>>
>>> sorted(data)
[1, 2, 3]
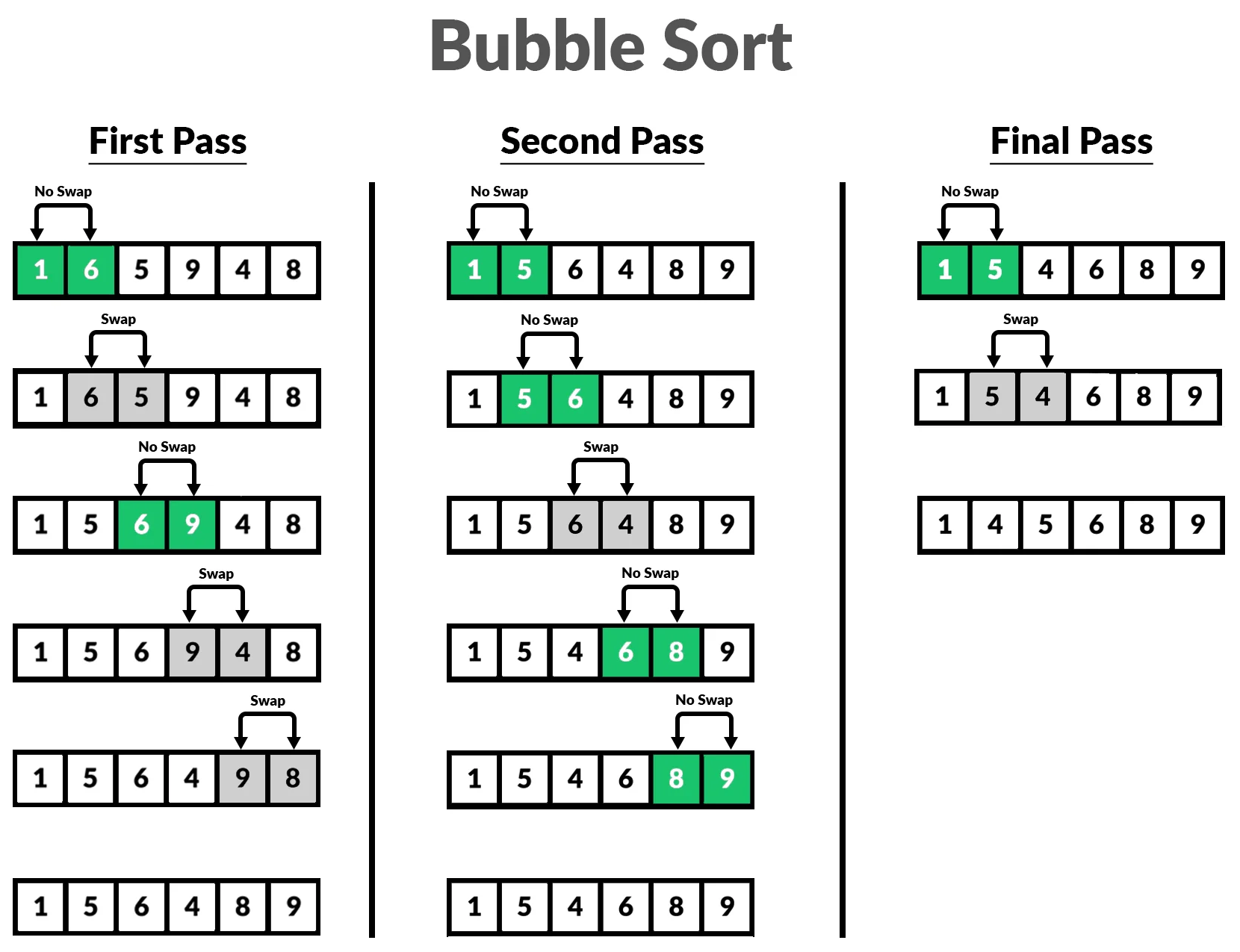
9.6.6. Bubble Sort
>>> def bubblesort(arr):
... result = arr.copy()
... n = len(arr)
... for i in range(n):
... for j in range(n-i-1):
... if result[j] > result[j+1]:
... result[j], result[j+1] = result[j+1], result[j]
... return result
9.6.7. Merge Sort
>>> def mergesort(arr):
... if len(arr) <= 1:
... return arr
...
... mid = len(arr) // 2
... left = mergesort(arr[:mid])
... right = mergesort(arr[mid:])
...
... result = []
... i = j = 0
...
... while i < len(left) and j < len(right):
... if left[i] < right[j]:
... result.append(left[i])
... i += 1
... else:
... result.append(right[j])
... j += 1
...
... result.extend(left[i:])
... result.extend(right[j:])
... return result
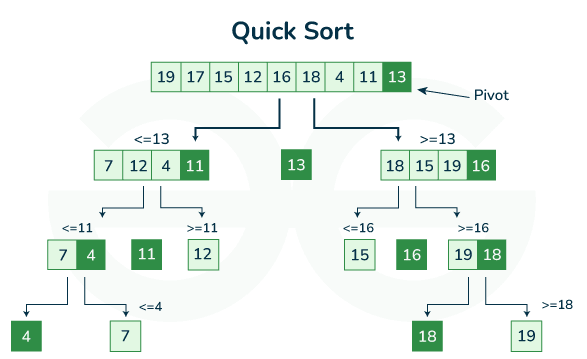
9.6.8. Quick Sort
>>> def quicksort(arr):
... if len(arr) <= 1:
... return arr
...
... pivot = arr[len(arr) // 2]
... left = [x for x in arr if x < pivot]
... middle = [x for x in arr if x == pivot]
... right = [x for x in arr if x > pivot]
...
... return quicksort(left) + middle + quicksort(right)
9.6.9. Tim Sort
Tim Peters
>>> def timsort(arr):
... min_run = 32
... n = len(arr)
...
... def insertion_sort(arr, left, right):
... for i in range(left + 1, right + 1):
... key = arr[i]
... j = i - 1
... while j >= left and arr[j] > key:
... arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
... j -= 1
... arr[j + 1] = key
...
... def merge(arr, left, mid, right):
... len1, len2 = mid - left + 1, right - mid
... left_part, right_part = arr[left:left + len1], arr[mid + 1:mid + 1 + len2]
...
... i = j = 0
... k = left
...
... while i < len1 and j < len2:
... if left_part[i] <= right_part[j]:
... arr[k] = left_part[i]
... i += 1
... else:
... arr[k] = right_part[j]
... j += 1
... k += 1
...
... while i < len1:
... arr[k] = left_part[i]
... i += 1
... k += 1
...
... while j < len2:
... arr[k] = right_part[j]
... j += 1
... k += 1
...
... for start in range(0, n, min_run):
... end = min(start + min_run - 1, n - 1)
... insertion_sort(arr, start, end)
...
... size = min_run
... while size < n:
... for left in range(0, n, 2 * size):
... mid = min(n - 1, left + size - 1)
... right = min((left + 2 * size - 1), (n - 1))
...
... if mid < right:
... merge(arr, left, mid, right)
...
... size *= 2
...
... return arr
9.6.10. References
9.6.11. Assignments
# %% About
# - Name: Idiom Sorted Sequence
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 1
# - Minutes: 2
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Use function `sorted()` to sort `DATA` in ascending order
# 2. Define variable `result` with the result
# 3. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Użyj funkcji `sorted()`, aby posortować `DATA` w porządku rosnącym
# 2. Zdefiniuj zmienną `result` z wynikiem
# 3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> result
# [1, 2, 3]
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> result
[1, 2, 3]
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
result: list[int]
# %% Data
DATA = [3, 1, 2]
# %% Result
result = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Idiom Sorted Reverse
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 1
# - Minutes: 2
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Use function `sorted()` to sort `DATA` in descending order
# 2. Define variable `result` with the result
# 3. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Użyj funkcji `sorted()`, aby posortować `DATA` w porządku malejącym
# 2. Zdefiniuj zmienną `result` z wynikiem
# 3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> result
# [3, 2, 1]
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> result
[3, 2, 1]
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
result: list[int]
# %% Data
DATA = [3, 1, 2]
# %% Result
result = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Idiom Sorted Key
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 3
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Use function `sorted()` to sort `DATA` by age in ascending order
# 2. Define variable `result` with the result
# 3. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Użyj funkcji `sorted()`, aby posortować `DATA` po wieku (age) w porządku rosnącym
# 2. Zdefiniuj zmienną `result` z wynikiem
# 3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> result
# [{'firstname': 'Mallory', 'lastname': 'Melon', 'age': 15},
# {'firstname': 'Alice', 'lastname': 'Apricot', 'age': 30},
# {'firstname': 'Bob', 'lastname': 'Blackthorn', 'age': 31},
# {'firstname': 'Carol', 'lastname': 'Corn', 'age': 32},
# {'firstname': 'Dave', 'lastname': 'Durian', 'age': 33},
# {'firstname': 'Eve', 'lastname': 'Elderberry', 'age': 34}]
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> pprint(result, sort_dicts=False)
[{'firstname': 'Mallory', 'lastname': 'Melon', 'age': 15},
{'firstname': 'Alice', 'lastname': 'Apricot', 'age': 30},
{'firstname': 'Bob', 'lastname': 'Blackthorn', 'age': 31},
{'firstname': 'Carol', 'lastname': 'Corn', 'age': 32},
{'firstname': 'Dave', 'lastname': 'Durian', 'age': 33},
{'firstname': 'Eve', 'lastname': 'Elderberry', 'age': 34}]
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
result: list[dict[str, str|int]]
# %% Data
DATA = [
{'firstname': 'Alice', 'lastname': 'Apricot', 'age': 30},
{'firstname': 'Bob', 'lastname': 'Blackthorn', 'age': 31},
{'firstname': 'Carol', 'lastname': 'Corn', 'age': 32},
{'firstname': 'Dave', 'lastname': 'Durian', 'age': 33},
{'firstname': 'Eve', 'lastname': 'Elderberry', 'age': 34},
{'firstname': 'Mallory', 'lastname': 'Melon', 'age': 15},
]
# %% Result
result = ...